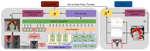
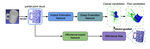
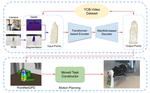
Summary
The term crossmodal learning refers to the adaptive, synergistic integration of complex perceptions from multiple sensory modalities, such that the learning that occurs within any individual sensory modality can be enhanced with information from one or more other modalities. Crossmodal learning is crucial for human understanding of the world, and examples are ubiquitous, such as: learning to grasp and manipulate objects; learning to read and write; learning to understand language; etc. In all these examples, visual, auditory, somatosensory or other modalities have to be integrated.